Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML markup language for structurally describing two-dimensional vector graphics. In essence, SVG is to graphics what HTML is to text. SVG is a W3C recommendation and is explicitly designed to work with other W3C standards such as HTML, CSS or DOM.
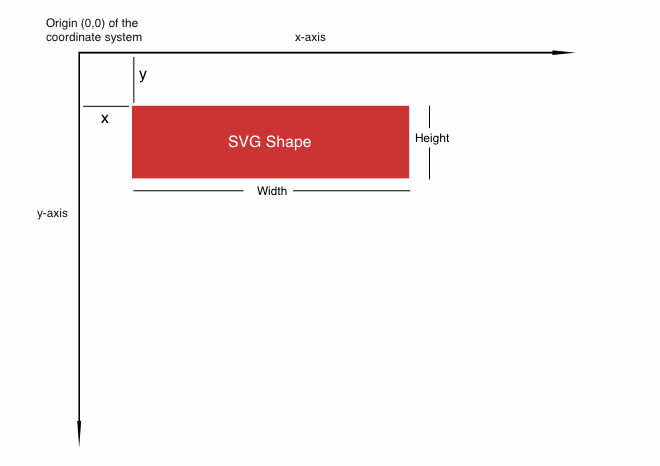
SVG Coordinate system
<svg width="50" height="50"> <!-- width and height of svg set to 50 -->
<circle cx="25" cy="25" r="20"/> <!-- Add circle at 25, 25 with radius=20 -->
</svg>
<svg width="50" height="50">
<circle cx="25" cy="25" r="20"
fill="blue"/> <!-- fill with circle with blue -->
</svg>
<svg width="50" height="50" >
<circle cx="25" cy="25" r="20"
fill="blue"
stroke="gray" stroke-width="5"/> <!-- Add 5px gray stroke -->
</svg>
A reaminder! All this SVG code goes inside the <body> tag.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>My first SVG</title>
</head>
<body>
<svg style="border:1px solid red;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50"/>
</svg>
</body>
</html>
There are a number of visual elements (rect, circle, ellipse, line, text, and path) that you can used to create something like:
There are no "layers" in SVG. The order in which elements are ordered determines the rendering order.